Dredging is defined as cleaning out the bed of a body of water by scooping out silt, mud, trash or other materials. While the objectives of dredging vary from deepening harbors and waterways to excavation and reclamation, it always results in a certain amount of dredged material being left over after the project is complete. In fact, each year, more than 100 million cubic yards of material is dredged from our country’s busy waterways, marinas, harbors and ports alone. That doesn’t even include the sand, clay, dirt and trash dredged from other bodies of water not associated with marine traffic such as ponds, lakes and reservoirs.
What to Do With Sediment After Dredging
Knowing this, it’s only logical that many of our customers ask what to do with sediment after dredging. Fortunately, after being in business for more than 20 years and supplying high-quality dredging and pumping systems to customers around the world, this is a question we’re well-equipped to answer.
It’s important to understand that while some dredged material is contaminated and deposited in confined disposal facilities (CDFs), a significant amount of it can be reused. Now, exactly how you reuse it depends on your objective, as well as whether the dredged material is a waste product, a recovered product or byproduct, or a primary product.
Waste Product from Dredging
If the dredged material is a waste product, there are several ways it can be used. For example, sand can be used for beach nourishment — in other words, to enhance existing beaches where the shoreline is threatened by erosion or even to create new beaches. It can also be used in combination with geotextile tubes to build out flood defenses on beaches.
Finer materials such as clay and fine dirt also have many applications. Fine clay material can be used for land creation and construction fill, especially for new land areas within harbors and ports. Fine dirt is also often mixed with additives such as manure, biosolids or compost to create or enhance topsoil.
Recovered Product or Byproduct
If your objective is to recover a product — in other words, to harvest or gather materials — there’s a wide range of potential uses depending on the product. The same goes for products that are a byproduct of your primary objective with the dredging operation.
For example, dredging is commonly used to harvest peat moss, which is used throughout the world as fuel or to enhance soil. Dredging is also used to recover biosolids — organic materials made from sewage — to create fertilizer.
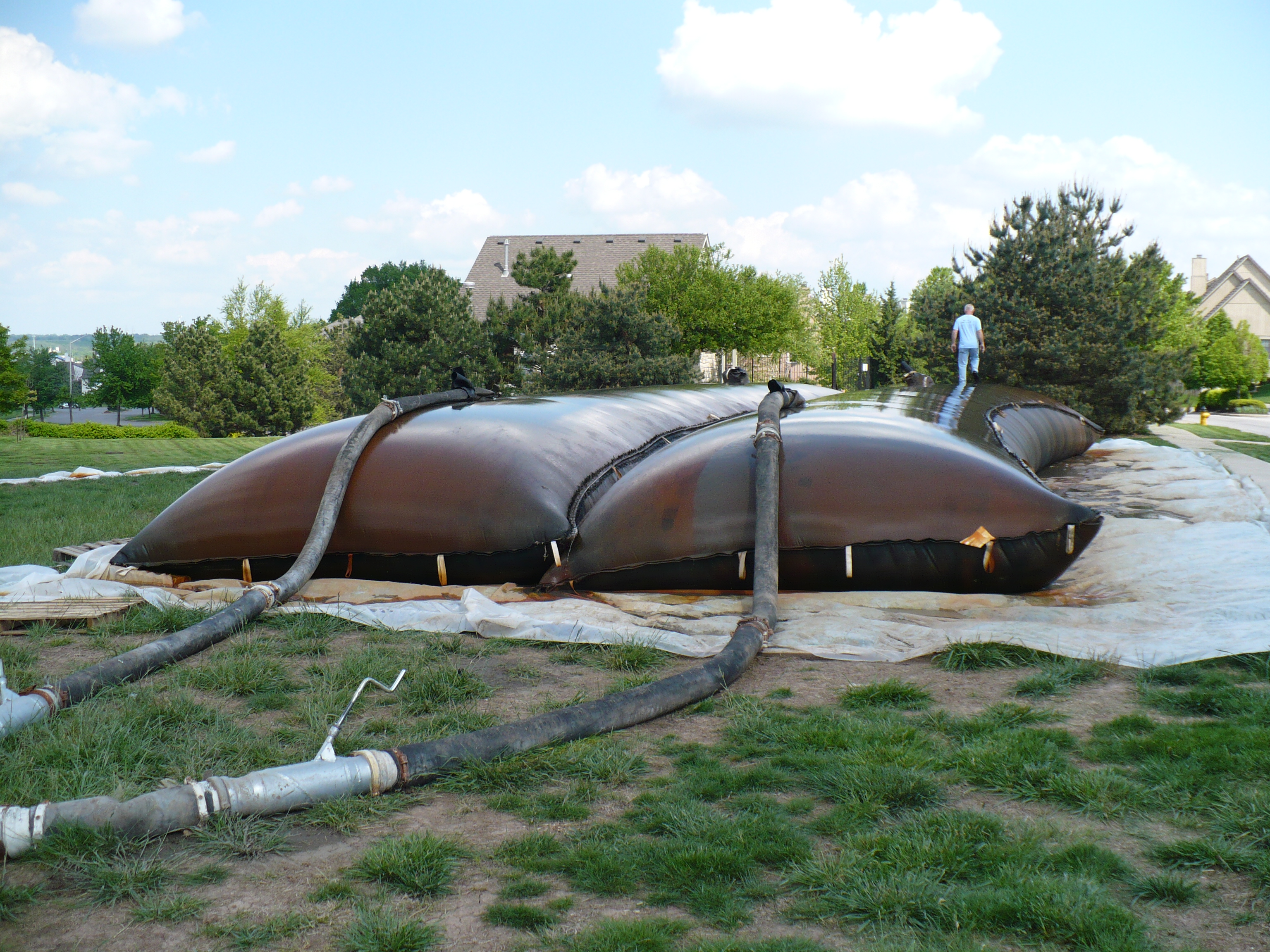
Here’s another interesting example: One of our customers is a golf course that used the Dino6 to dredge all of its ponds. While doing so, they recovered approximately five 55-gallon drums worth of golf balls, most of which were still in perfectly usable condition!
Primary Product
If you’re mining or dredging for a primary product, there are several potential uses for the dredged materials. Sand, for example, is gathered for a range of production purposes, including the making of glass or as a component in mortar. Dredged material can also include other fine granules — including precious metals like gold.
Contact Us for More Information
Clearly, there are many different uses for dredged materials depending on the materials themselves and your objective. If you have any further questions about dredged material uses or any of our products, contact our team of experts today!


 Dino6
Dino6  Dino8
Dino8  Submersible Pumps
Submersible Pumps